Operational
We strive to improve our performance annually across key environmental metrics to deliver superior value to all stakeholders. Our goals and practices associated with greenhouse gas emissions, energy intensity, recycling and water use demonstrate our commitment to best-in-class performance and reducing our operational footprint.
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS & ENERGY INTENSITY
We are committed to reducing our carbon footprint through the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In 2024, we reduced combined Scope 1 and 2 thanks to continued investment in energy Efficiency projects within our operations.
Absolute Metric Tons CO2e of GHG
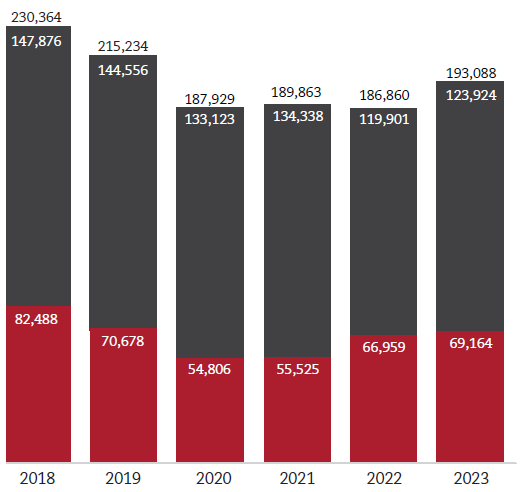
in Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 2025
from 2018 to 2024
- Scope 1
- Scope 2
RECYCLING & LANDFILL AVOIDANCE
We aspire to achieve zero waste from our operations. Our waste management program prioritizes a "reduce, reuse and recycle" approach to divert waste from landfills, leverage waste as a resource, and increase recycling in our operations.
This includes expanding the use of our waste as a feedstock for third parties and introducing collection and handling systems that allow us to capture and reuse materials. We measure the percentage of all waste that we can reuse or recycle, the percentage of permissible waste1 that can be diverted from landfills, and the percentage of hazardous waste.
- Permissible waste is waste that is non-hazardous (per the local country definition).
Total Recycling & Landfill Avoidance Rates
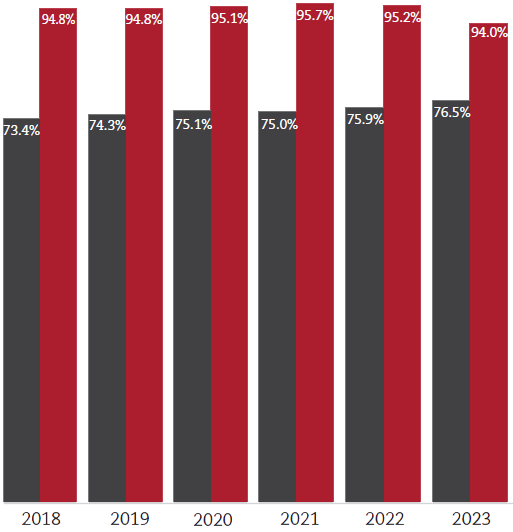
- Total Recycling Rate
- Landfill Avoidance Percentage
WATER MANAGEMENT
Water is an important natural resource and we acknowledge our responsibility to manage water carefully. Water is predominantly used in our consumable manufacturing processes. We monitor and measure absolute water use and water intensity (cubic meters of water used per hour worked).
Water Withdrawal (cubic meters)
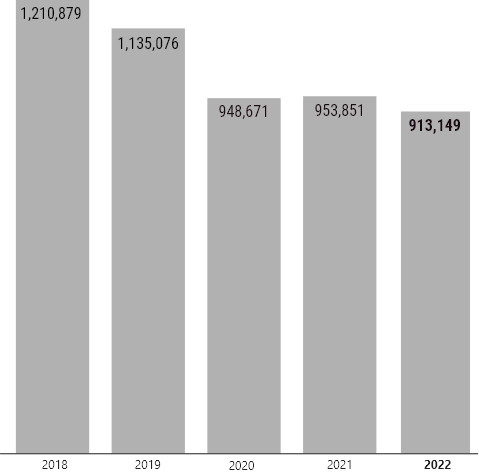
in water withdrawal by 2025
from 2018 to 2024